Server architecture
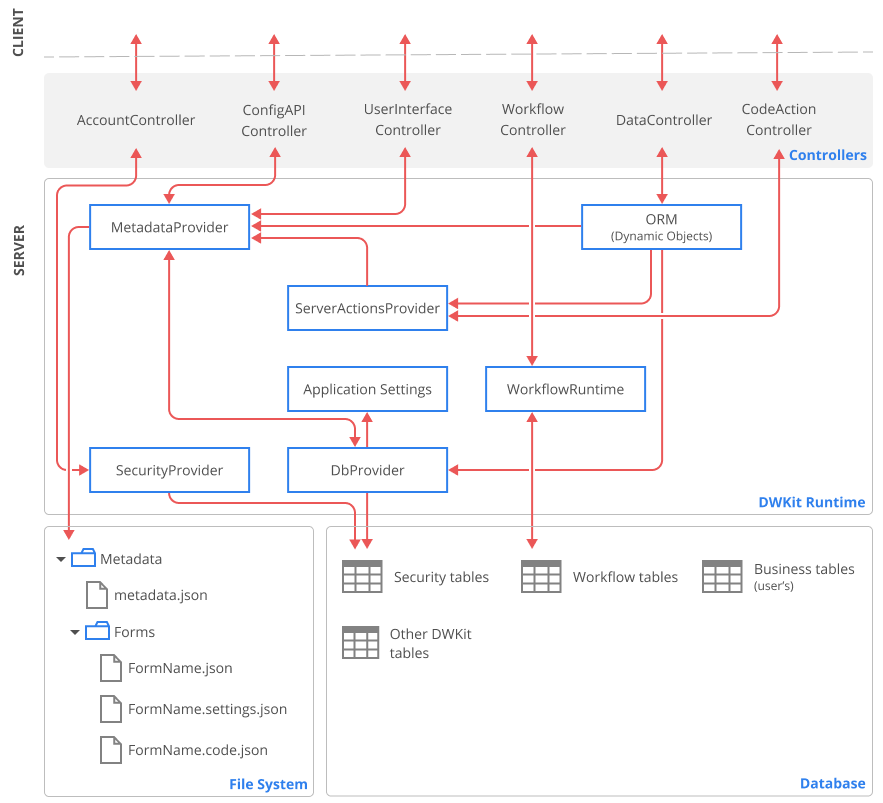
MVC Controllers represent a front-end interface for the server side of DWKit. We've already mentioned them earlier.
UserInterfaceController- getting of a form via theGetFormmethod. It also receives form by business flow name, usingGetFlowmethod.DataController- getting data via theGetDatamethod, changingdatavia theChangeDatamethod, deletingdatavia theDeleteDatamethod. It also containsGetDictionarymethod for transmitting data to components (for example, Dictionary and Tree picker) andUploadFileandDownloadFilemethods used to work with files.WorkflowController- getting a list of commands and states via theGetDatamethod, execution of commands via theExecuteCommandmethod, setting states via theSetStatemethod.ConfigAPIController- controller, via which the Admin application saves and loads metadata.AccountController- is responsible for signing in and signing out. Read more about security in DWKit here.CodeActionController- launches server actions from client. Learn more here.
On the server side, you will mainly interact with two entities: DWKitRuntime static class and
an ORM subsystem. DWKitRuntime is the key point of configuration and locator of the system services of DWKit,
such as:
MetadataProvider- inherits theIMetadataProviderinterface, enables to save metadata and transfer them to the application. Any component of DWKit that needs system metadata requests them from this service. In DWKit, metadata is stored in the following locations:- metadata.json file - serialized Data model, Server user-defined actions, Business flows are stored here.
- Descriptions of Forms are stored in the Forms subfolder. Each form can contain 1-3 files.
- MyFormName.json - a serialized form layout, i.e. contains settings of all form components and their positions.
- MyFormName-settings.json - workflow settings and binding of data model to form controls.
- MyFormName-code.js - client actions handlers code.
- The metadata related to Security is stored in the database in
dwSecurity*tables.
ApplicationSettings- enables access to connection strings, cache settings, license key, etc. It is not a separate service; all these settings can be customized via the Dashboard page in the Admin application.WorkflowRuntime- main Workflow Engine object that manages processes. Learn more about Workflow Engine's architecture.ServerActionsProvider- enables access to server user actions, such as server filters, triggers or server actions. Learn more here. You can write these actions code in the Admin application or in your projects, implementing theIServerActionsProviderinterface and registering your provider in the mainServerActionsProvider.DbProvider- enables physical communication with the database, processes all database queries except for those coming fromWorkflowRuntime, which uses its own providers. Distribution includes providers for MS SQL Server, PostgreSQL and Oracle.SecurityProvideris responsible for getting information about authorized users and checking their permissions.
There are several system tables in the database:
dwSecurity...tables - store security system description. For more details, see this section.dwAppSettings- table in which some of DWKit settings are stored.dwUploadedFiles- table to store files which are uploaded via DWKit app interface.Workflow...tables - these are Workflow Engine tables. Check out their description.
The DWKitRuntime object should be configured. It has already been done in the OptimaJet.DWKit.Application project, the Configurator
class. Check out its code
on GitHub. Now, let's go
through its key points.
public static class Configurator
{
public static void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IConfigurationRoot configuration, string connectionStringName = "default")
{
var httpContextAccessor = (IHttpContextAccessor)app.ApplicationServices.GetService(typeof(IHttpContextAccessor));
var notificationHubContext = (IHubContext<ClientNotificationHub>)app.ApplicationServices.GetService(typeof(IHubContext<ClientNotificationHub>));
var eventService = (IEventService)app.ApplicationServices.GetService(typeof(IEventService));
var authenticationSchemeProvider = (IAuthenticationSchemeProvider)app.ApplicationServices.GetService(typeof(IAuthenticationSchemeProvider));
var ldap = configuration.GetSection("LDAPConf").Get<Security.IdentityProvider.LDAPConf>();
if (notificationHubContext != null)
{
DWKitRuntime.HubContext = notificationHubContext;
}
var security = new DefaultSecurityProvider(httpContextAccessor, eventService, authenticationSchemeProvider, ldap);
Configure(security, configuration, connectionStringName);
}
private static void Configure(ISecurityProvider security, IConfigurationRoot configuration, string connectionstringName = "default")
{
#region License
var licensefile = "license.key";
if (File.Exists(licensefile))
{
var licenseText = File.ReadAllText(licensefile);
DWKitRuntime.RegisterLicense(licenseText);
}
#endregion
#if (DEBUG)
DWKitRuntime.UseMetadataCache = false;
//CodeActionsCompiler.DebugMode = true;
#elif (RELEASE)
DWKitRuntime.UseMetadataCache = true;
#endif
DWKitRuntime.ConnectionStringData = configuration[$"ConnectionStrings:{connectionstringName}"];
DWKitRuntime.DbProvider = AutoDetectProvider();
DWKitRuntime.Security = security;
var path = configuration["Metadata:path"];
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(path))
{
path = "Metadata/metadata.json";
}
DWKitRuntime.Metadata = new DefaultMetadataProvider(path, "Metadata/Forms", "Metadata/Localization");
...
if (!string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(configuration["DWKit:CodeActionsDebugMode"]))
{
DWKitRuntime.CodeActionsDebugMode = bool.Parse(configuration["DWKit:CodeActionsDebugMode"]);
}
CodeActionsCompiler.RegisterAssembly(typeof(WorkflowRuntime).Assembly);
// It is necessary to have this assembly for compile code with dynamic
CodeActionsCompiler.RegisterAssembly(typeof(Microsoft.CSharp.RuntimeBinder.Binder).Assembly);
DWKitRuntime.CompileAllCodeActionsAsync().Wait();
DWKitRuntime.ServerActions.RegisterUsersProvider("filters", new Filters());
DWKitRuntime.ServerActions.RegisterUsersProvider("triggers", new Triggers());
...
}
public static IDbProvider AutoDetectProvider()
{
...
return provider;
}
}
-
DWKitRuntime.RegisterLicense(licenseText);- registers a license key read from the file. -
This code turns on/off metadata caching, depending on build configuration. Given that the conversion from Data Model or Mapping form and data into metadata format used by the ORM is a frequent and time-consuming procedure, it will be reasonable to turn caching on in the RELEASE configuration to speed things up.
#if (DEBUG)
DWKitRuntime.UseMetadataCache = false;
#elif (RELEASE)
DWKitRuntime.UseMetadataCache = true;
#endif -
DWKitRuntime.ConnectionStringData = configuration[$"ConnectionStrings:{connectionstringName}"]- gets a connection string from the configuration file. -
DWKitRuntime.DbProvider = AutoDetectProvider();- automatic creation of theDbProviderby the connection string. -
var security = new DefaultSecurityProvider(httpContextAccessor, eventService, authenticationSchemeProvider, ldap);- creation of theDefaultSecurityProviderwith access to theHttpContextand configured access to external resources via LDAP. -
DWKitRuntime.Metadata = new DefaultMetadataProvider("Metadata/metadata.json", "Metadata/Forms", "Metadata/Localization");- creation of theMetadataProviderwith specified path names that lead tometadata.json, form metadata and localization files. -
registration of server user actions and compilation of those created in the Admin application.
if (!string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(configuration["DWKit:CodeActionsDebugMode"]))
{
DWKitRuntime.CodeActionsDebugMode = bool.Parse(configuration["DWKit:CodeActionsDebugMode"]);
}
CodeActionsCompiler.RegisterAssembly(typeof(WorkflowRuntime).Assembly);
// It is necessary to have this assembly for compile code with dynamic
CodeActionsCompiler.RegisterAssembly(typeof(Microsoft.CSharp.RuntimeBinder.Binder).Assembly);
DWKitRuntime.CompileAllCodeActionsAsync().Wait();
DWKitRuntime.ServerActions.RegisterUsersProvider("filters", new Filters());
DWKitRuntime.ServerActions.RegisterUsersProvider("triggers", new Triggers());